As owner of Rophe Pharma, Gadimian is passionate about educating people on the fantastic benefits of fish oil. He understands the complicated science of why fish oil is good for you but he can also break it down into a way normal people talk and heal.
Los Angeles, California, August 3, 2017 (Newswire.com) - Stopping inflammation is a key component
What we understand as inflammation, scientists describe this complex process as “stopping the arachidonic acid cascade.” And yup, fish oil does that.
Fish oil: the good fat omega-3
Our bodies don’t create the essential oils omega-3 and omega-6, so we get it from our diet. Meat and vegetable oil are the most common dietary sources of omega-6. Omega-3 acids are mainly found in seafood and fish oil. A ‘good acid’ would be the fish-sourced omega-3 fatty acids known as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Fish oil: fights bad fat omega-6
The omega-6 fatty acids can convert to arachidonic acid which is a “bad” fat. Arachidonic acids are found primarily in fatty red meats, egg yolks, and organ meats. This polyunsaturated fat is thought to be the most dangerous fat when consumed in excess.
It is important to block bad fat effects
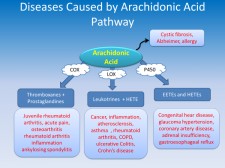
Arachidonic acid is the precursor for arachidonic acid cascade that plays a major role in a variety of diseases (including cancer) in different organs of the body (Figure 1). It is the precursor of eicosanoids, an important group of biologically active compounds. Eicosanoids are derivatives formed in the arachidonic acid cascade. The arachidonic acid cascade is the cause of many illnesses (Figure 1). Eicosanoids are formed by three different routes, namely via the cyclooxygenase (COX), cytochrome P-450 (cyt P-450) or lipoxygenase (LOX) pathways. The eicosanoids are considered "local hormones." They have specific effects on target cells close to their site of formation.
Examples of eicosanoids are prostaglandins, prostacyclins, thromboxanes, leukotrienes, and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (ETEs). They have roles in inflammation, fever, regulation of blood pressure, blood clotting, immune system modulation, control of reproductive processes and tissue growth, and regulation of the sleep/wake cycle and may play a role in cancer, asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune disorders. (Figure 1).
Fish oil: the amazing health benefits
How does fish oil help us with the negative impact of arachidonic acid? Gadimian explains that, as EPA and DHA found in the fish oil are incorporated into cellular membranes throughout the body, they do two things. First, they displace arachidonic acid and second, they compete with arachidonic acid for conversion into metabolites. When the DHA and EPA compete with arachidonic acid, they are thought to prevent the activation of the arachidonic acid cascade, which is the root cause of many diseases. This means that fish oil not only prevents heart disease, it may prevent other diseases.
The clinically effective dose of DHA and EPA is around 1-2 grams per day.
Figure 1: Illustration of the three pathways in the classical arachidonic acid cascade and the related diseases in each pathway.
Source: Robert Gadimian
Share: